Group Leader: Carmen Gianfrani
Topics: Immunity and Infection
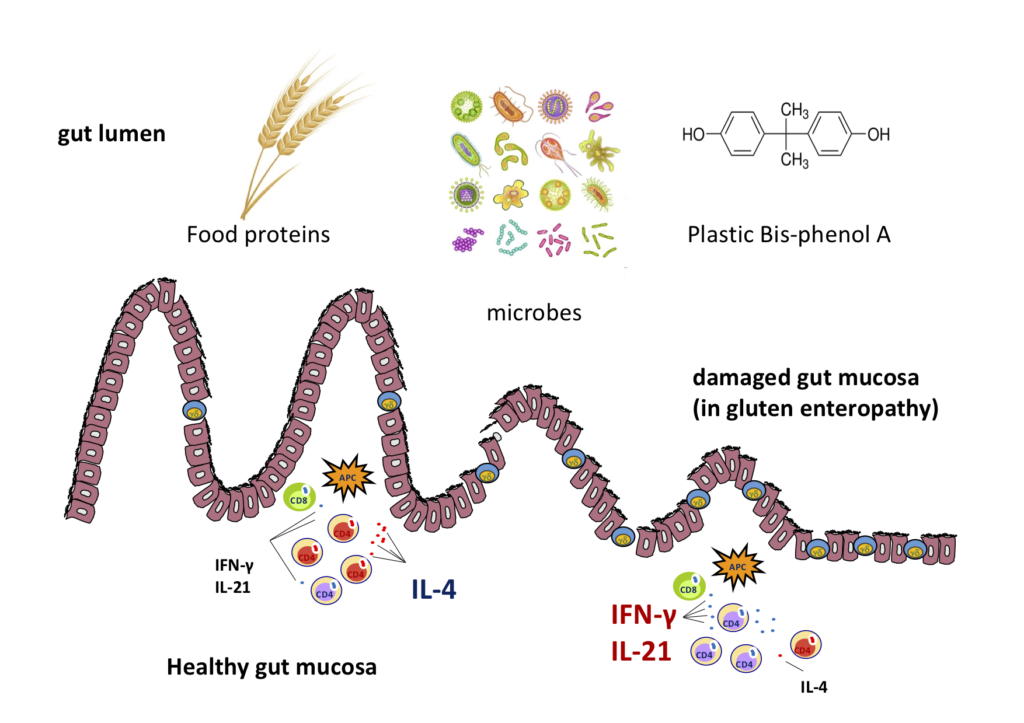
MIIN LAB, is a mucosal immunologist interested in studying the interaction between food proteins and gastrointestinal immune system. Her research is mainly focused on the disregulation of immune tolerance to wheat gluten and on defining immunomodulatory strategies to recover the oral tolerance to gluten in celiac disease patients. Particularly, Dr Gianfrani has contributed to develop enzymatic strategies to detoxify wheat gluten that are currently in clinical trials.
Dr Gianfrani is also interested to investigate the role of HLA risk gene expression in the inflammatory response to gluten proteins, with implication for celiac disease prevention. In the recent years, Dr Gianfrani’s LAB has been interested in the immunopathogenesis of paediatric inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), in particular on the role of ATG16L1 gene polymorphisms in autophagy alteration in IBD patients. Dr Gianfrani has co-authored more than 70 original papers and reviews in international journals, as well as of book chapters on mucosal immunology and organic chemistry. Dr Gianfrani is the author of several articles and reviews for science outreach, and of interviews to mass media, as expert of celiac disease.
The main scientific interests of MIIN LAB are:
- Immune pathogenesis of celiac disease and pediatric inflammatory bowel disease
- Role of HLA class II gene expression in shaping the pathogenic immune response in autoimmunity
- Characterization of gluten peptides stimulating helper and cytotoxic T cell response in celiac disease patients
- Identification of ancient wheat crops with reduced content of toxic gluten sequences and with high in vivo digestibility
Key Pubblications
Picascia S, Camarca A, Malamisura M, Mandile R, Galatola M, Cielo D, Gazza L, Mamone G, Auricchio S, Troncone R, Greco L, Auricchio R, Gianfrani C. In Celiac Disease Patients the In Vivo Challenge With the Diploid Triticum Monococcum Elicits a Reduced Immune Response Compared to Hexaploid Wheat. Mol Nutr&Food Res 2020. doi: 10.1002/mnfr.201901032.
Vitale S, Santarlasci V, Camarca A, Picascia S, Di Pasquale A, Maglio M, Maggi E, Cosmi L, Annunziato F, Troncone R, Auricchio R, Gianfrani C. The intestinal expansion of TCRγδ+ and disappearance of IL4+ T cells suggest their involvement in the evolution from potential to overt celiac disease. Eur J Immunol. 2019. doi: 10.1002/eji.201948098.
Pisapia L, Camarca A, Picascia S, Bassi V2, Barba P, Del Pozzo G, Gianfrani C. HLA-DQ2.5 genes associated with celiac disease risk are preferentially expressed with respect to non-predisposing HLA genes: Implication for anti-gluten T cell response. J Autoimmun. 2016. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2016.03.016.
Strisciuglio C, Miele E, Wildenberg M.E, Giugliano F.P, Andreozzi M, Vitale A, Capasso F, Camarca A, Barone M.V, Staiano A, Troncone R, Gianfrani C. T300A variant of autophagy ATG16L1 gene is associated with decreased antigen sampling and processing by dendritic cells in paediatric Crohn’s disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis, 2013. doi: 10.1097/MIB.0b013e3182a6a11c.
Mazzarella G, Stefanile R, Camarca A, Giliberti P, Casentini E, Marano C, Iaquinto G, Giardullo N, Auricchio S, Sette A, Troncone R, Gianfrani C. Gliadin activates HLA Class I-restricted CD8+ T-cells in coeliac intestinal mucosa and induces the enterocyte apoptosis. Gastroenterology. 2008.
Research Group

Post-doctoral fellows:
Stefania Picascia stefania.picascia@ibbc.cnr.it
Serena Vitale serena.vitale@ibbc.cnr.it
Graduate student:
Ilaria Mottola (University Federico II, Naples)
Program & Resources
- Italian Ministry of University and Research PNR 2011- 2013. Flagship Interomics 2015 and 2017.
- Italian Association of Celiac Disease (AIC/FC), 2017
- Italian Ministry of Health. Bando Ricerca Finalizzata, 2016.
- National Health and Medical Research Council Australia – NHMRC, 2012.
- Italian Ministry of University and Research, PRIN, 2009.
