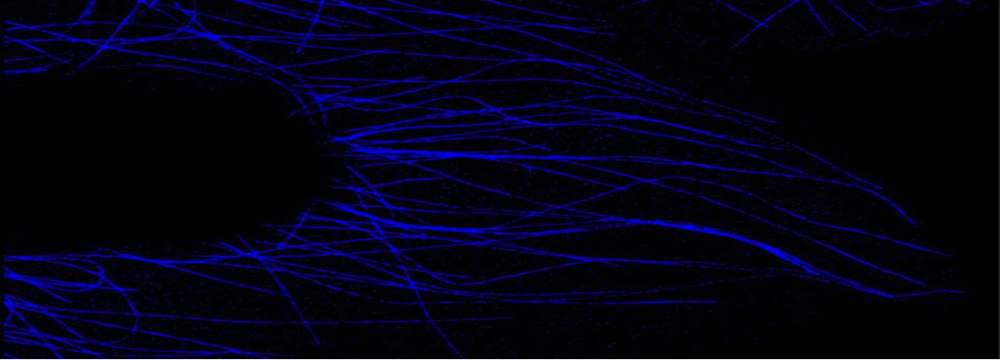
Euro-bioimaging ERIC infrastructure
Welcome to the Naples Euro-BioImaging ERIC facility located at the IBBC in CNR Research area NA-1. The facility is a continuation of the imaging facility developed by Alberto Luini and colleagues at the Mario Negri Sud Institute for Biomedical Research in the 1990s that pioneered the development of the modern Correlative video-Light Electron Microscopy (CLEM). It is the coordinating facility of the Advanced Light Microscopy Italian multi-modal multi-sited Node of Euro-BioImaging, a pan European research infrastructure project (for more information see: http://www.eurobioimaging.eu/). It is managed and operated by the IBBC. The Naples Euro-BioImaging facility (and all other Euro-BioImaging facilities in the participating countries) started their interim operation since May 2016. The Naples facility can be accessed through the Euro-BioImaging portal or following the instruction reported here.
Brigthfield, Phase contrast, DIC and confocal microscopy
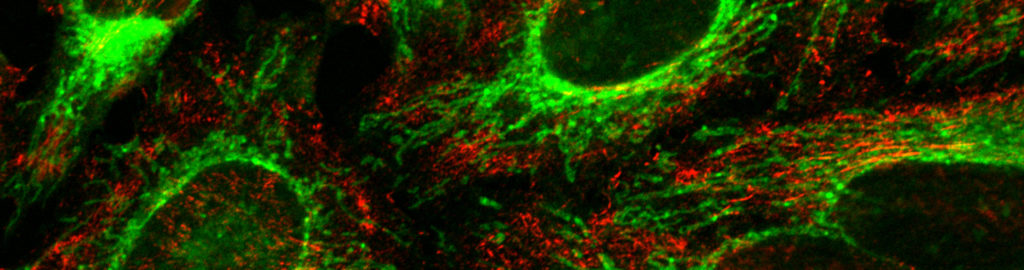
The facility is equipped with a phase contrast and DIC microscope, and two laser scanning confocal microscopes. All the systems have the temperature and CO2 control module, required for live imaging studies. The IBBC users will be provided batch training once in a year in the use of the routine ligth microscopes.
Services provided:
- Bright-field, DIC and phase-contrast microscopy, for evaluation of general morphology and enzyme-based labelling of cells and tissues;
- Wide-field fluorescence microscopy, for analysis of fluorescent marker distributions in cells and tissues;
- Confocal microscopy, to investigate co-localisation of proteins and their three-dimensional (3D) space distribution
- Image analysis station equipped with Zen off line analysis program, AxioVision off line analysis program, Leica image analysis suite, Image J, Cell profiler and Metamorph image analysis software.
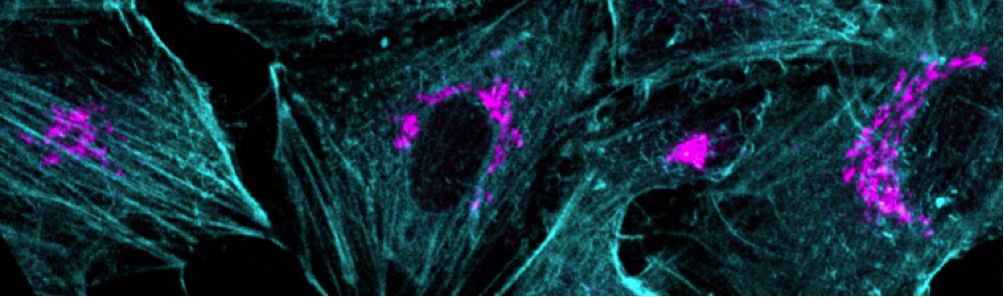
High speed confocal 4D imaging, spectral analysis, super-resolution imaging, imaging multiprotein complexes by multiplexing FRET/FLIM
The facility is equipped with two laser scanning confocal microscopes, one spinning disc confocal microscope and a structured-illumination based microscope. All the microscopes are equipped with temperature and CO2 control modules necessary for live imaging studies. The IBBC users will be provided batch training once in a year in the use of confocal microscopes and the apotome microscope and if sufficient numbers of people are present more additional courses will be considered. For the use of other microscopes individual training will be provided in case of need.
Services provided
- Live-cell imaging (time-lapse microscopy), for monitoring intracellular organelles and protein dynamics in time and in 3D space;
- Video Microscopy including Fluorescence recovery after photobleaching (FRAP) and Fluorescence Loss in Photobleaching (FLIP) for quantitative evaluation of protein mobility within organelles, rates of inter-organelle exchange, and protein binding kinetics;
- Fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) and Fluorescence Lifetime Imaging (FLIM) , to evaluate the strength and intracellular topology of protein-protein interactions, and monitor intracellular dynamics of small signalling molecules and protein activities;
- Lambda imaging;
- Super resolution imaging (G-STED);
- Cell microinjection, for acute modulation (activation or inhibition) of protein activities;
- Image analysis station equipped with Zen off line analysis program, AxioVision off line analysis program, Leica image analysis suite, Image J, Cell profiler and Metamorph image analysis software.
Access to Facility
For internal users:
Only certified independent users are allowed to use the microscopes.
Each certified user will be provided with a magnetic card to access the facility.
New users will have to participate in the annual training course on the use of microscopes before they will be allowed to access the facility. If you are not a certified user and you need to use the microscope, you can do so with the help of another experienced user from your group. Alternatively, you can contact the facility members for support.
Booking the microscopes:
Each research group is allotted timeslots to use the microscopes. The allocation chart can be found here.
These slots can be booked online.
The slots should be booked no later than 9:00 AM of that day; else the slot is considered free and other users may book the turn
The slots that have been booked should be occupied within 15min of the start of the booking time, else other users will be to free use the slot. Bookings need to be cancelled at least 24h in advance, else you will be charged for the use. In case you need more than the allotted time, you can book the free turns or time
The free slots should not be booked more than 48h in advance.
Fee:
The charges for the use of the microscope and facility can be found here.
The costs of any damage to the instruments or the facility will be charged to the user.
For external users:
Being a part of the Euro-BioImaing network the requests from external users (other than IBBC) needs to be routed through the Euro-BioImaging portal. Details about this can be found here
We also encourage the potential users to contact the facility before so as to prepare the application together. Please write an email to this address: bioimaging@ibbc.cnr.it
You will be contacted by our staff as soon as possible to guide you through the procedures
For publications:
Depending on the nature of the request, an authorship in the eventual publication may be required. Please discuss about this with the facility head before starting the project.
In any case (whether an authorship is provided or not) we request the users to please acknowledge the use of the BioImaging facility by inserting the following in the “Acknowledgement section” of their publications: “We thank the Euro-BioImaging facility at the Institute of Protein Biochemistry (CNR), Naples for help with microscopy experiments.”
Selected Publications (2019-2020)
- Swartzwelter BJ, Barbero F, Verde A, Mangini M, Pirozzi M, De Luca AC, Puntes VF, Leite LCC, Italiani P, Boraschi D. Gold Nanoparticles Modulate BCG-Induced Innate Immune Memory in Human Monocytes by Shifting the Memory Response towards Tolerance. Cells. 2020 Jan 23;9(2). pii: E284.
- Loria AD, Dattilo V, Santoro D, Guccione J, De Luca A, Ciaramella P, Pirozzi M, Iaccino E. Expression of Serum Exosomal miRNA 122 and Lipoprotein Levels in Dogs Naturally Infected by Leishmania infantum: A Preliminary Study. Animals (Basel). 2020 Jan 8;10(1). pii: E100.
- Chiritoiu M, Brouwers N, Turacchio G, Pirozzi M, Malhotra V. GRASP55 and UPR Control Interleukin-1β Aggregation and Secretion. Dev Cell. 2019 Apr 8;49(1):145-155.e4.
- Subramanian A, Capalbo A, Iyengar NR, Rizzo R, di Campli A, Di Martino R, Lo Monte M, Beccari AR, Yerudkar A, Del Vecchio C, Glielmo L, Turacchio G, Pirozzi M, Kim SG, Henklein P, Cancino J, Parashuraman S, Diviani D, Fanelli F, Sallese M, Luini A. Auto-regulation of Secretory Flux by Sensing and Responding to the Folded Cargo Protein Load in the Endoplasmic Reticulum. Cell. 2019 Mar 7;176(6):1461-1476.
- Sesorova IS, Karelina NR, Kazakova TE, Parashuraman S, Zdorikova MA, Dimov ID, Seliverstova EV, Beznoussenko GV, Mironov AA. Structure of the enterocyte transcytosis compartments during lipid absorption. Histochem Cell Biol. 2020 Mar 11.
- Parashuraman S, D’Angelo G. Visualizing sphingolipid biosynthesis in cells. Chem Phys Lipids. 2019 Jan;218:103-111.
- Pothukuchi P, Agliarulo I, Russo D, Rizzo R, Russo F, Parashuraman S. Translation of genome to glycome: role of the Golgi apparatus. FEBS Lett. 2019 Sep;593(17):2390-2411.
- Lania G, Nanayakkara M, Maglio M, Auricchio R, Porpora M, Conte M, De Matteis MA, Rizzo R, Luini A, Discepolo V, Troncone R, Auricchio S, Barone MV. Constitutive alterations in vesicular trafficking increase the sensitivity of cells from celiac disease patients to gliadin. Commun Biol. 2019 May 20;2:190.
- Varone A, Mariggiò S, Patheja M, Maione V, Varriale A, Vessichelli M, Spano D, Formiggini F, Lo Monte M, Brancati N, Frucci M, Del Vecchio P, D’Auria S, Flagiello A, Iannuzzi C, Luini A, Pucci P, Banci L, Valente C, Corda D. A signalling cascade involving receptor-activated phospholipase A2, glycerophosphoinositol 4-phosphate, Shp1 and Src in the activation of cell motility. Cell Commun Signal. 2019 Mar 1;17(1):20.
- Tapia D, Jiménez T, Zamora C, Espinoza J, Rizzo R, González-Cárdenas A, Fuentes D, Hernández S, Cavieres VA, Soza A, Guzmán F, Arriagada G, Yuseff MI, Mardones GA, Burgos PV, Luini A, González A, Cancino J. KDEL receptor regulates secretion by lysosome relocation- and autophagy-dependent modulation of lipid-droplet turnover. Nat Commun. 2019 Feb 13;10(1):735.
- Catara G, Grimaldi G, Schembri L, Spano D, Turacchio G, Lo Monte M, Beccari AR, Valente C, Corda D. PARP1-produced poly-ADP-ribose causes the PARP12 translocation to stress granules and impairment of Golgi complex functions. Sci Rep. 2017 Oct 25;7(1):14035.
- Campelo F, van Galen J, Turacchio G, Parashuraman S, Kozlov MM, García-ParajoMF, Malhotra V.
Sphingomyelin metabolism controls the shape and function of the Golgi cisternae. Elife. 2017 May 13;6. pii: e24603 - Filadi R, Greotti E, Turacchio G, Luini A, Pozzan T, Pizzo P.
On the role of Mitofusin 2 in endoplasmic reticulum-mitochondria tethering. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017 Mar 21;114(12):E2266-E2267 - Brandolini L, d’Angelo M, Antonosante A, Villa S, Cristiano L, Castelli V, Benedetti E, Catanesi M, Aramini A, Luini A, Parashuraman S, Mayo E, Giordano A, Cimini A, Allegretti M.
Differential protein modulation by ketoprofen and ibuprofen underlines different cellular response by gastric epithelium. J Cell Physiol. 2018 Mar;233(3):2304-2312. - Campelo F, van Galen J, Turacchio G, Parashuraman S, Kozlov MM, García-Parajo MF, Malhotra V.
Sphingomyelin metabolism controls the shape and function of the Golgi cisternae. Elife. 2017 May 13;6. pii: e24603 - Hegde RN, Subramanian A, Pothukuchi P, Parashuraman S, Luini A. Rare ER protein misfolding-mistrafficking disorders: Therapeutic developments. Tissue Cell. 2017 Apr;49(2 Pt A):175-185.
- Rizzo R, Parashuraman S, D’Angelo G, Luini A.
GOLPH3 and oncogenesis: What is the molecular link? Tissue Cell. 2017 Apr;49(2 Pt A):170-174. - Capasso S, Sticco L, Rizzo R, Pirozzi M, Russo D, Dathan NA, Campelo F, van Galen J, Hölttä‐Vuori M, Turacchio G, Hausser A, Malhotra V, Riezman I, Riezman H, Ikonen E, Luberto C, Parashuraman S, Luini A and D’Angelo G.
Sphingolipid metabolic flow controls phosphoinositide turnover at the trans‐Golgi network. EMBO J. May 2, 36 (9): 1117–1297 (2017) - Filadi R, Greotti E, Turacchio G, Luini A, Pozzan T, Pizzo P. On the role of Mitofusin 2 in endoplasmic reticulum-mitochondria tethering. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017 Mar 21;114(12):E2266-E2267.
- Raote I, Ortega Bellido M, Pirozzi M, Zhang C, Melville D, Parashuraman S, Zimmermann T, Malhotra V.TANGO1 assembles into rings around COPII coats at ER exit sites.J Cell Biol. 2017 Mar 9; 216 (3).
- Gaglio D, Valtorta S, Ripamonti M, Bonanomi M, Damiani C, Todde S, Negri AS, Sanvito F, Mastroianni F, Di Campli A, Turacchio G, Di Grigoli G, Belloli S, Luini A, Gilardi MC, Colangelo AM, Alberghina L, Moresco RM. Divergent in vitro/in vivo responses to drug treatments of highly aggressive NIH-Ras cancer cells: a PET imaging and metabolomics-mass-spectrometry study. Oncotarget. 2016 Aug 9;7(32):52017-52031.
- Chesi G, Hegde RN, Iacobacci S, Concilli M, Parashuraman S, Festa BP, Polishchuk EV, Di Tullio G, Carissimo A, Montefusco S, Canetti D, Monti M, Amoresano A, Pucci P, van de Sluis B, Lutsenko S, Luini A, Polishchuk RS. Identification of p38 MAPK and JNK as new targets for correction of Wilson disease-causing ATP7B mutants. Hepatology. 2016 Jun;63(6):1842-59.
- Schiattarella GG, Cattaneo F, Pironti G, Magliulo F, Carotenuto G, Pirozzi M,, Polishchuk R, Borzacchiello D, Paolillo R, Oliveti M, Boccella N, Avvedimento M, Sepe M, Esposito G, Trimarco B, Feliciello A, Perrino C. Akap1 deficiency promotes mitochondrial aberrations and exacerbates cardiac injury following permanent coronary ligation via enhanced mitophagy and apoptosis. PLoS One. May 2, 11 (5) (2016).
- Curwin AJ, Brouwers N, Alonso Y Adell M, Teis D, Turacchio G,Parashuraman S, Ronchi P, Malhotra V. ESCRT-III drives the final stages of CUPS maturation for unconventional protein secretion. Elife. 2016 Apr 26;5
- Filadi R, Greotti E, Turacchio G, Luini A, Pozzan T, Pizzo P. Mitofusin 2 ablation increases endoplasmic reticulum-mitochondria coupling. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015 Apr 28;112(17):E2174-81.
- Chrisam M, Pirozzi M, Castagnaro S, Blaauw B, Polishchuck R, Cecconi F, Grumati P, Bonaldo P. Reactivation of autophagy by spermidine ameliorates the myopathic defects of collagen VI-null mice. Autophagy. 2015;11(12):2142-52.
- Hegde RN, Parashuraman S, Iorio F, Ciciriello F, Capuani F, Carissimo A, Carrella D, Belcastro V, Subramanian A, Bounti L, Persico M, Carlile G, Galietta L, Thomas DY, Di Bernardo D, Luini A. Unravelling druggable signalling networks that control F508del-CFTR proteostasis. Elife. 2015 Dec 23;4.

